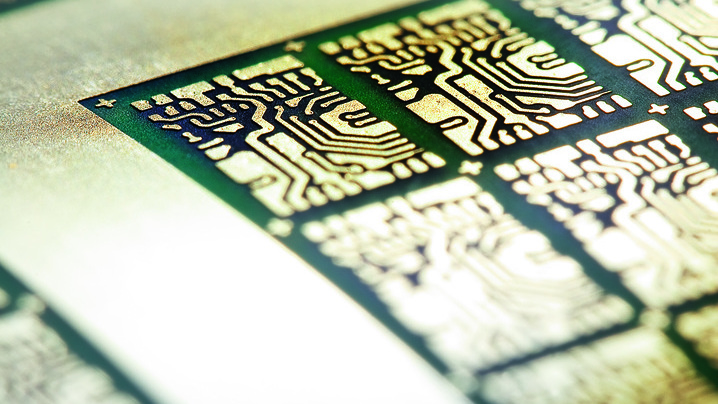
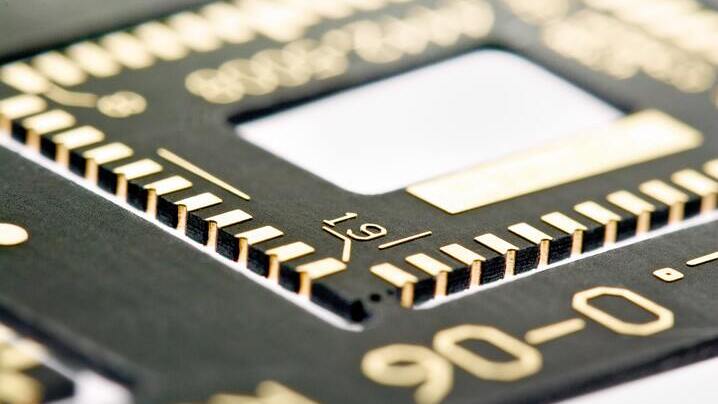
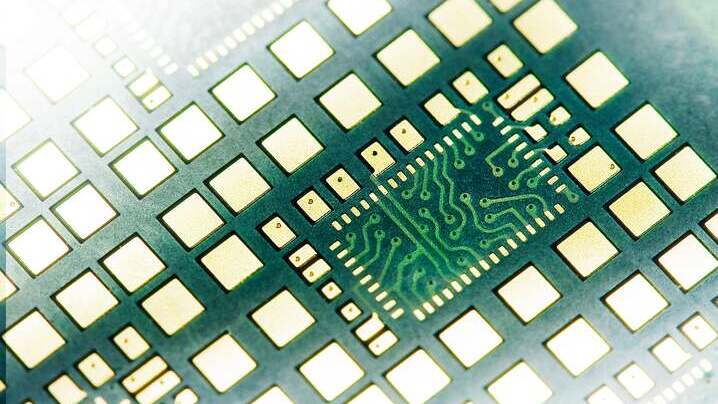
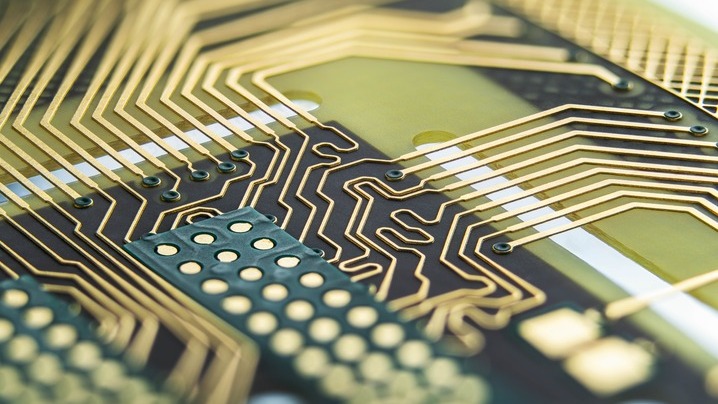
Rigid Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are a type of circuit board characterized by their stiffness and inability to be bent. As the most common type of PCB, they are integral to a wide array of electronic devices. When these PCBs have more than two layers, they are referred to as multilayer PCBs. Constructed from solid, non-flexible substrate materials like fiberglass reinforced epoxy resin (e.g., FR4), rigid PCBs offer superior dimensional stability and enhanced high-frequency performance.
Adding features like cavities, castellations, or flying leads can further enhance the functionality and versatility of rigid PCBs. Cavities are recesses or pockets that can embed components, reducing the overall thickness of the PCB or offering protection to the embedded elements. Castellations are half-plated holes along the edges of the board, allowing for easy soldering onto a PCB. Flying leads are conductors extending beyond the edge of the PCB, offering flexibility during prototyping and debugging stages, as well as in low-volume products.